[Runtime] Class, Object 与 isa
Table of Contents
作为 Runtime 系列的第一篇博文(也是 2022 年第一篇),先从最基础的对象、类开始学习。
参考 OC 编译过程 我们可以借助 clang 工具将 OC 源码预处理成 CPP 来窥探 OC 的内部实现。
定义一个简单的类:
@interface Foo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign) BOOL ppty1;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *ppty2;
- (BOOL)iMethod1;
- (void)iMethod2:(NSString *)p1;
+ (void)cMethod1;
@end
通过命令 clang -rewrite-objc xx.m 得到一个 9 万多行的 cpp 文件 😱
https://gist.github.com/ryderfang/75a852f1ae0961aeea97127f7d9ca6c5
TL;DR #
太长不看版:
🧸 objc_object 是所有实例对象的底层结构,内部只有一个 isa
🎁 objc_class 是所有类/元类对象的底层结构,它也有一个 isa 指针,指向自己的元类
| OC 1.0 | OC 2.0 | |
|---|---|---|
| id 实例 | typedef struct objc_object *id; | typedef struct objc_object *id; |
| objc_object | struct objc_object {} | struct objc_object {} |
| Class 类 | typedef struct objc_class *Class; | typedef struct objc_class *Class; |
| objc_class | struct objc_class {} | struct objc_class : objc_object {} |
Class 是什么 #
Class 1.0 #
在 <objc/objc.h> 中有这样一行:
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
在 iOS 15 之前 <objc/runtime.h> 中曾经有 objc_class 的定义:
https://opensource.apple.com/source/objc4/objc4-750/runtime/runtime.h.auto.html
/* Types */
#if !OBJC_TYPES_DEFINED
struct objc_class {
Class _Nonnull isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
#if !__OBJC2__
Class _Nullable super_class OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
const char * _Nonnull name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long version OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long info OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long instance_size OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_ivar_list * _Nullable ivars OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_method_list * _Nullable * _Nullable methodLists OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_cache * _Nonnull cache OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_protocol_list * _Nullable protocols OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#endif
} OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
/* Use `Class` instead of `struct objc_class *` */
#endif
目前我使用的 Xcode 13.2.1 中已经找不到这个定义,也就是说在 macOS 12.1 / iOS 15.2 中,OBJC1 已经被完全废弃。
Hint: 按照官方文档 Runtime Version 的解释, legacy 版本 (OC 1.0) 在 2007 年就完全废弃了,所有 iPhone 和 OSX 10.5 以后的 Mac 上使用的都是 modern 版本 (OC 2.0)!
根据 wiki 的说明,OC 2.0 于 2006 年发布,而 iPhone 第一代 是在 2007 年发布的,Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard 也是在 2007 年上市。
从这个宏 OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE 可以看出来 OBJC2 这种定义会失效。那么 OBJC2 是什么?
Class 2.0 #
在 objc-runtime-new.h 中定义了 objc_class 的 2.0 版本:
struct objc_class : objc_object {
// Class ISA;
Class superclass;
cache_t cache; // formerly cache pointer and vtable
class_data_bits_t bits; // class_rw_t * plus custom rr/alloc flags
class_rw_t *data() {
return bits.data();
}
...
}
了解到,苹果在 2006 年重写了 runtime,发布了新的 Runtime 2.0,那么 __OBJC2__ 这个宏是什么时候生效的呢?
通过查找苹果公开的 runtime 源码:https://opensource.apple.com/source/objc4/ 发现:
从 objc4-750 这个版本开始,在 objc-config.h 中开始有了 __OBJC2__ 的定义!
// Define __OBJC2__ for the benefit of our asm files.
#ifndef __OBJC2__
# if TARGET_OS_OSX && !TARGET_OS_IOSMAC && __i386__
// old ABI
# else
# define __OBJC2__ 1
# endif
#endif
来自 apple 的 commit:
https://github.com/apple-oss-distributions/objc4/commit/26c7408b94ead1f04a0b5976e354a03966ce61ea
在 objc-api.h 中定义了 OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY:
/* OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY: `isa` will be deprecated or unavailable
* in the future */
#if !defined(OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY)
# if __OBJC2__
# define OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY __attribute__((deprecated))
# else
# define OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY /* still available */
# endif
#endif
在 objc-private.h 中同时定义了 OBJC_TYPES_DEFINED:
/* Isolate ourselves from the definitions of id and Class in the compiler
* and public headers.
*/
#ifdef _OBJC_OBJC_H_
#error include objc-private.h before other headers
#endif
#define OBJC_TYPES_DEFINED 1
同时也定义了 Class 和 id
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
typedef struct objc_object *id;
所以,不管 OC 1.0 还是 2.0,
Class 都是一个叫
objc_class的结构体指针。
Object 与 id #
在 <objc/objc.h> 中,定义
https://opensource.apple.com/source/objc4/objc4-750/runtime/objc.h.auto.html
Object 1.0 #
#if !OBJC_TYPES_DEFINED
/// An opaque type that represents an Objective-C class.
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
/// Represents an instance of a class.
struct objc_object {
Class _Nonnull isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
};
/// A pointer to an instance of a class.
typedef struct objc_object *id;
#endif
同样被包在 OBJC_TYPES_DEFINED 宏中,也就是 OC 2.0 并不生效。
那么,OC 2.0 的 objc_object 是什么样的呢,在 objc-private.h 中定义了:
Object 2.0 #
struct objc_object {
private:
isa_t isa;
public:
// ISA() assumes this is NOT a tagged pointer object
Class ISA();
// initIsa() should be used to init the isa of new objects only.
// If this object already has an isa, use changeIsa() for correctness.
// initInstanceIsa(): objects with no custom RR/AWZ
// initClassIsa(): class objects
// initProtocolIsa(): protocol objects
// initIsa(): other objects
void initIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=false*/);
void initClassIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=maybe*/);
void initProtocolIsa(Class cls /*nonpointer=maybe*/);
void initInstanceIsa(Class cls, bool hasCxxDtor);
// 省略大量方法
private:
void initIsa(Class newCls, bool nonpointer, bool hasCxxDtor);
// 省略大量方法`
};
可以看出来不管 OC 1.0 还是 2.0,
objc_object 都是一个包含着一个叫 isa 指针/变量 的对象。
isa 又是什么 #
在 1.0 版本中 isa 就是一个 Class 对象,也就是一个指向 objc_class 的指针,而在 2.0 时,isa 是一个叫 isa_t 的结构体变量。
那么 isa_t 是什么呢?
同样在 objc-private.h 中有定义:
union isa_t {
isa_t() { }
isa_t(uintptr_t value) : bits(value) { }
uintptr_t bits;
private:
// Accessing the class requires custom ptrauth operations, so
// force clients to go through setClass/getClass by making this
// private.
Class cls;
public:
#if defined(ISA_BITFIELD)
struct {
ISA_BITFIELD; // defined in isa.h
};
bool isDeallocating() {
return extra_rc == 0 && has_sidetable_rc == 0;
}
void setDeallocating() {
extra_rc = 0;
has_sidetable_rc = 0;
}
#endif
void setClass(Class cls, objc_object *obj);
Class getClass(bool authenticated);
Class getDecodedClass(bool authenticated);
};
参考 1 的图:
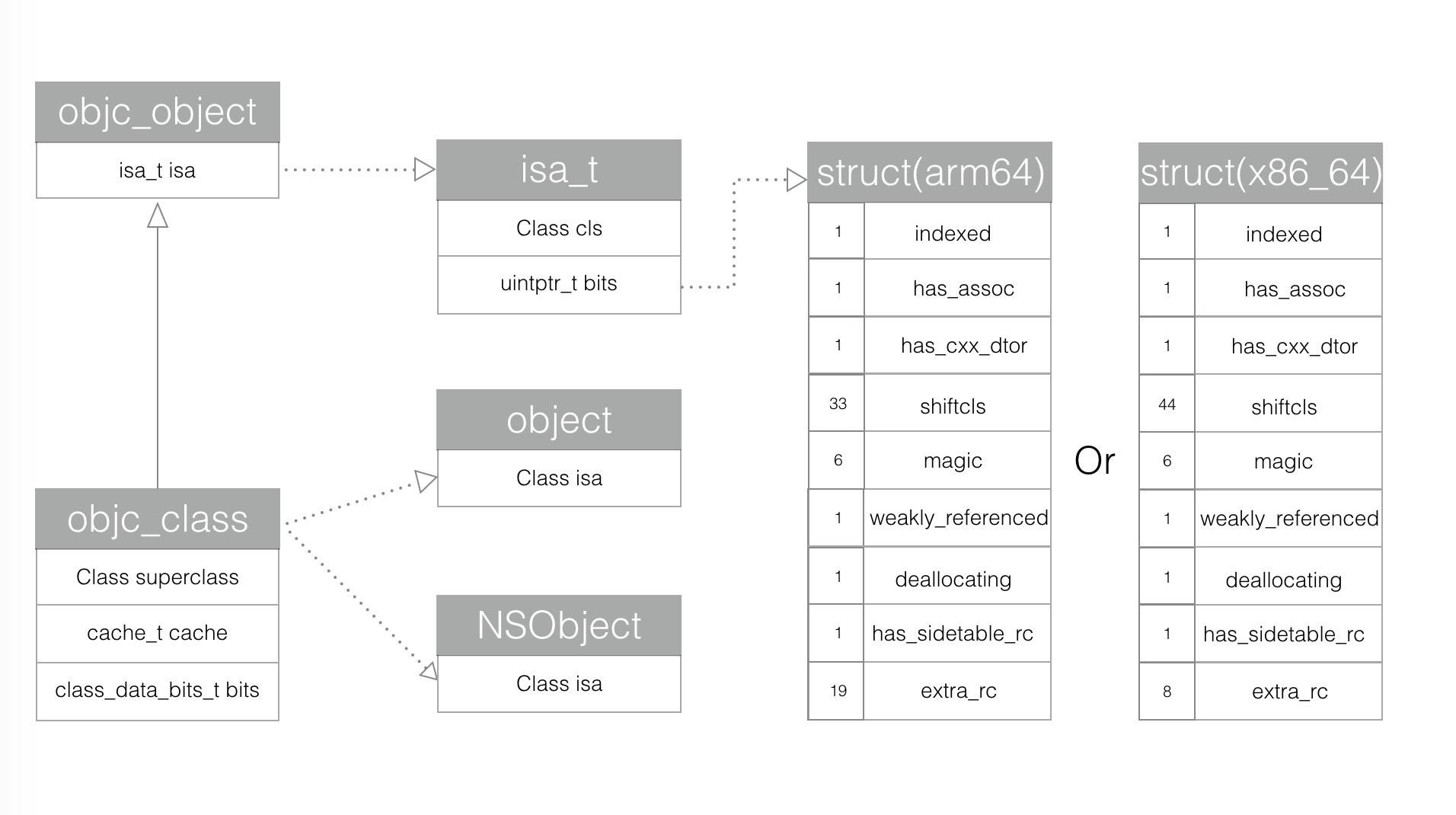
作为一个 union 结构,与 struct 区别在于,成员之间会互相覆盖,union 的总内存占用等于最大的成员占用的内存大小,而 struct 大小至少是成员内存占用之和,如果需要字节对齐则会更大。
所以采用 union 结构可以节省内存。
在 objc-object.h 中,有 objc_object::initIsa() 的实现:
inline void
objc_object::initIsa(Class cls, bool nonpointer, bool hasCxxDtor)
{
ASSERT(!isTaggedPointer());
if (!nonpointer) {
isa = isa_t((uintptr_t)cls);
} else {
ASSERT(!DisableNonpointerIsa);
ASSERT(!cls->instancesRequireRawIsa());
isa_t newisa(0);
#if SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
ASSERT(cls->classArrayIndex() > 0);
newisa.bits = ISA_INDEX_MAGIC_VALUE;
// isa.magic is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
// isa.nonpointer is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
newisa.has_cxx_dtor = hasCxxDtor;
newisa.indexcls = (uintptr_t)cls->classArrayIndex();
#else
newisa.bits = ISA_MAGIC_VALUE;
// isa.magic is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
// isa.nonpointer is part of ISA_MAGIC_VALUE
newisa.has_cxx_dtor = hasCxxDtor;
newisa.shiftcls = (uintptr_t)cls >> 3;
#endif
// This write must be performed in a single store in some cases
// (for example when realizing a class because other threads
// may simultaneously try to use the class).
// fixme use atomics here to guarantee single-store and to
// guarantee memory order w.r.t. the class index table
// ...but not too atomic because we don't want to hurt instantiation
isa = newisa;
}
}
可以看出 isa_t 中的 Class 与 bits 是互斥的,避免了互相覆盖的问题。