树的结构与算法之二:构造
·379 words·2 mins·
📖
Table of Contents
上文介绍了树的遍历,这次说一下如何从数组构造树结构。
层次构造 #
一般测试数据的输入是数组,我们需要将数组转换成树结构。同时,为了便于输出验证,也需要将树再转回数组。
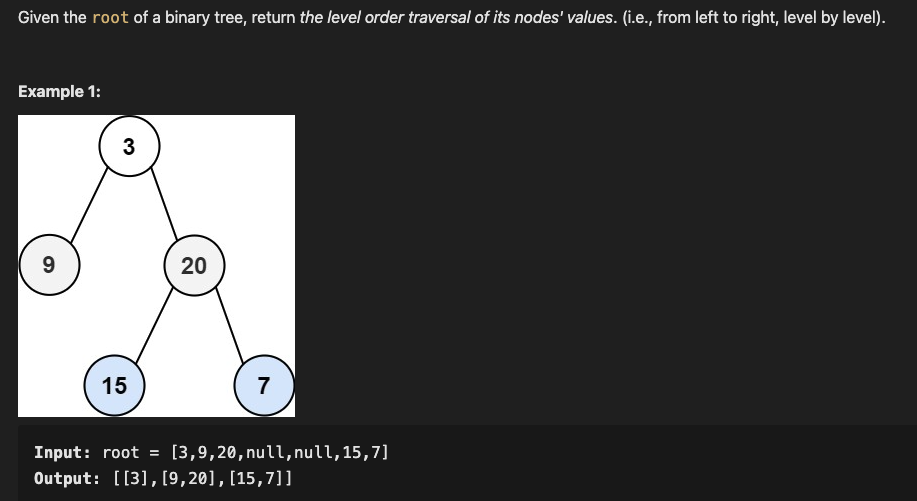
来源:102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
其实就是层次遍历及其逆向构造树的过程。
public extension TreeNode {
func array() -> [Int?] {
var ans: [Int?] = []
var queue: [TreeNode?] = [self]
while !queue.isEmpty {
if let node = queue.removeFirst() {
ans.append(node.val)
queue.append(node.left)
queue.append(node.right)
} else {
ans.append(nil)
}
}
// remove nils at last
while ans.last == nil {
ans.removeLast()
}
return ans
}
// TODO: to be optimized
static func arrayToTree(_ nums: [Int?]) -> TreeNode? {
guard nums.count > 0 else { return nil }
guard let rootVal = nums[0] else { return nil }
let root = TreeNode(rootVal)
var queue: [TreeNode?] = [root]
var i = 1
let sz = nums.count
while !queue.isEmpty && i < sz {
let node = queue.removeFirst()
if let val = nums[i] {
let left = TreeNode(val)
node?.left = left
queue.append(left)
}
i += 1
if i >= sz {
break
}
if let val = nums[i] {
let right = TreeNode(val)
node?.right = right
queue.append(right)
}
i += 1
}
return root
}
}
这个构造过程过于朴素,需要后续优化下 🥸
Update #
一种更 Swifter 的写法
func array() -> [Int?] {
var result = [Int?]()
var tree: [TreeNode?] = [self]
while !tree.isEmpty {
guard tree.compactMap({ $0 }).count > 0 else { break }
result.append(contentsOf: tree.map { $0?.val })
tree = tree.compactMap { $0 }.flatMap { [$0?.left, $0?.right] }
}
return result
}
前序与中序构造 #
105. Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
树的结构是递归的,所以大部分与树有关的问题,都是可以使用递归转化成子问题来求解。
前序是 根-左-右 的结构,而中序是 左-根-右,所以:
- 前序的第一位一定是根
- 根将中序分成了左子树中序和右子树中序
- 树的前序和中序长度一样,同样左右子树的前序和中序,长度也是一样的。
- 这样问题就转换成了:
- 确定根节点
- 分解成左子树和右子树两个子问题
- 递归调用本身
extension Solution {
func buildTree(pre preorder: [Int], _ inorder: [Int]) -> TreeNode? {
let n = preorder.count
guard n > 0 else { return nil }
let root = TreeNode(preorder[0])
guard let rootIdx = inorder.firstIndex(of: root.val) else { return nil }
if rootIdx > 0 {
root.left = buildTree(pre: Array(preorder[1...rootIdx]), Array(inorder[0..<rootIdx]))
}
root.right = buildTree(pre: Array(preorder[rootIdx+1..<n]), Array(inorder[rootIdx+1..<n]))
return root
}
}
中序与后序构造 #
106. Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
思路同上:
- 后序是
左-右-根,所以最后一位是根
extension Solution {
func buildTree(_ inorder: [Int], post postorder: [Int]) -> TreeNode? {
let n = inorder.count
guard n > 0 else { return nil }
let root = TreeNode(postorder[n-1])
guard let rootIdx = inorder.firstIndex(of: root.val) else { return nil }
if rootIdx > 0 {
root.left = buildTree(Array(inorder[0..<rootIdx]), post: Array(postorder[0..<rootIdx]))
}
root.right = buildTree(Array(inorder[rootIdx+1..<n]), post: Array(postorder[rootIdx..<n-1]))
return root
}
}